GNN学习记录_2
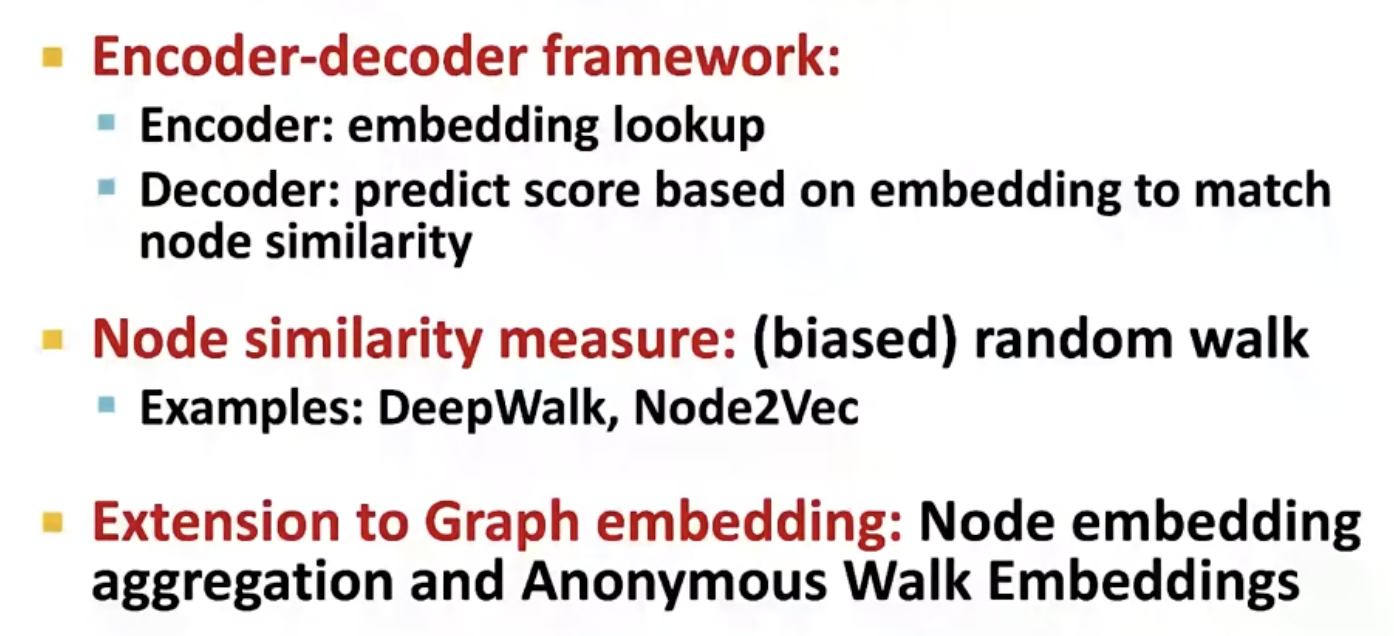
Embedding
Why Embedding
Task: map nodes into an embedding space .
Similarity of embeddings between nodes indicates their similarity in the network.
For example:
Both nodes are close to each other (connected by an edge)
Encode network information
Potentially used for many downstream predictions
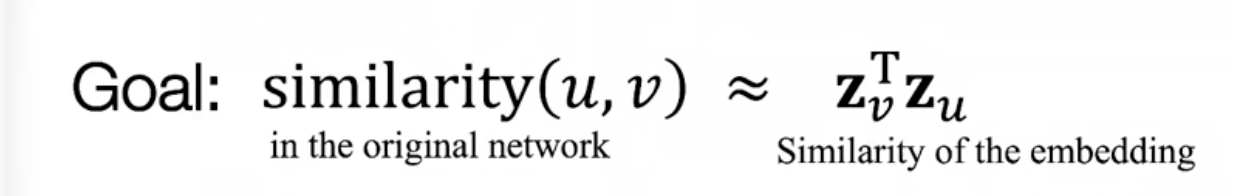
Random Walk
Random Walk is a method of embedding a graph.

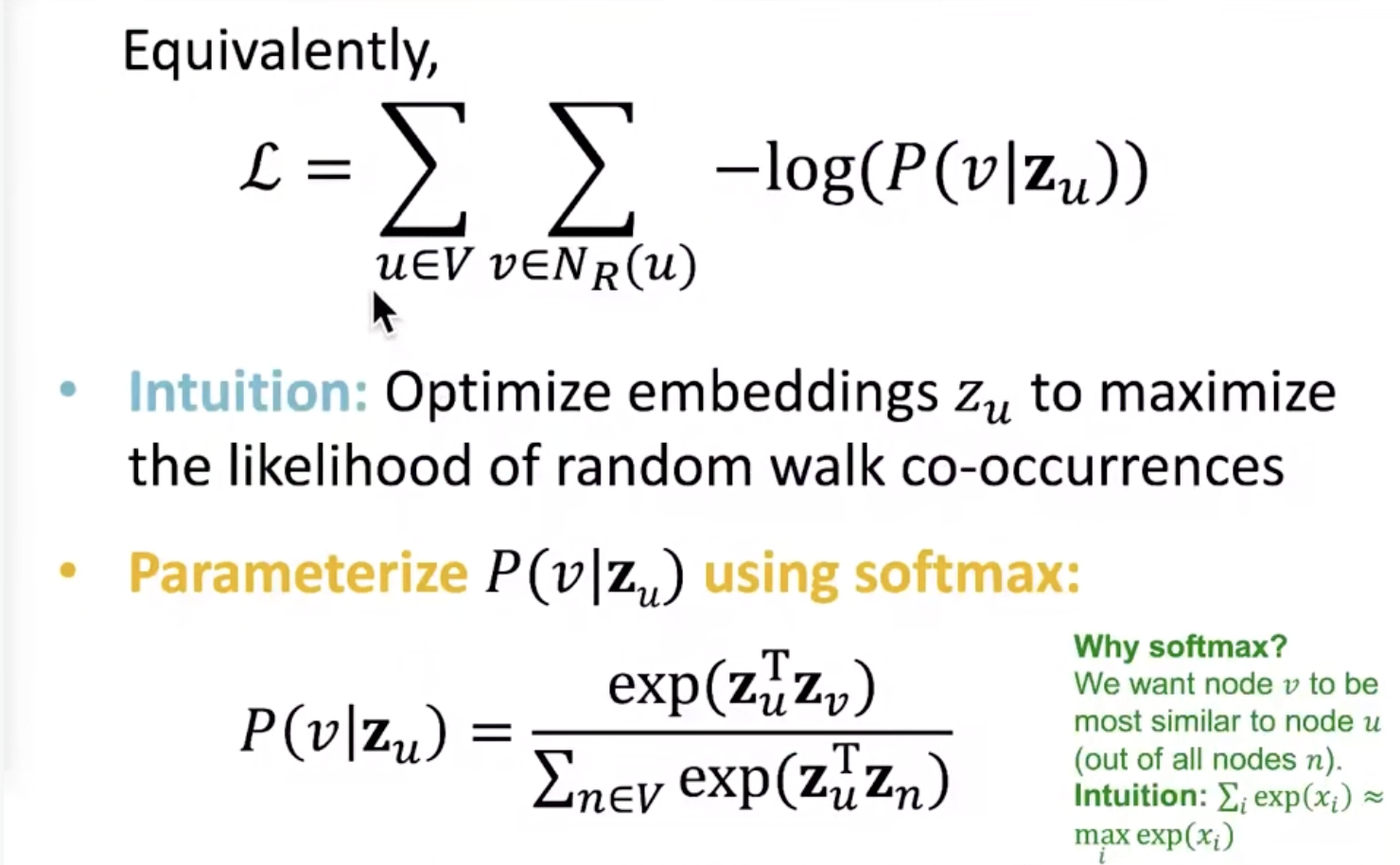
We have got the aiming function.Then we want to minimize the value of it using the ‘Stochastic Gradient Descent’.
How should we randomly walk?
Node2vec:
We change every node in the graph into a vector using the random walk.
Goal:Embed nodes with similar network neighborhoods close in the feature space.
Steps:
- Compute random walk probabilities.
- Simulate r random walks of length / starting from each node u.
- Optimize the node2vec objective using Stochastic Gradient Descent.
BFS and DFS:
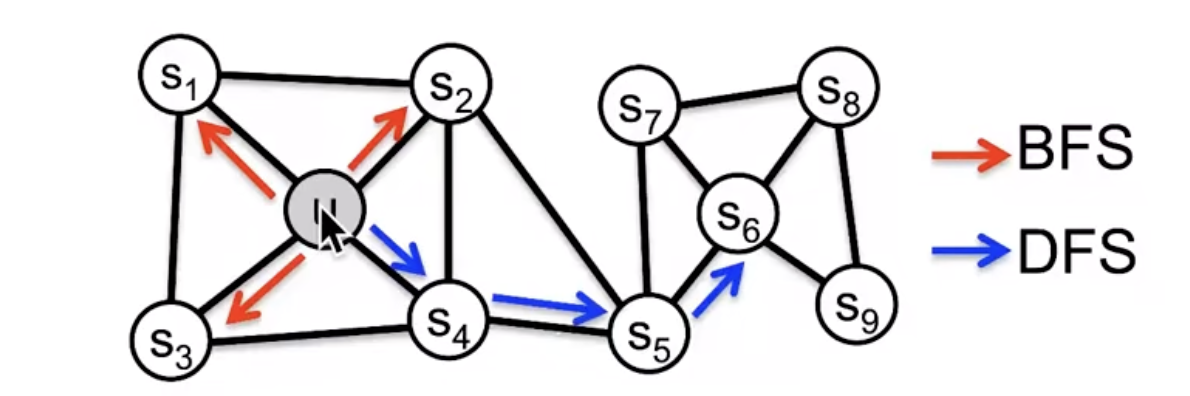
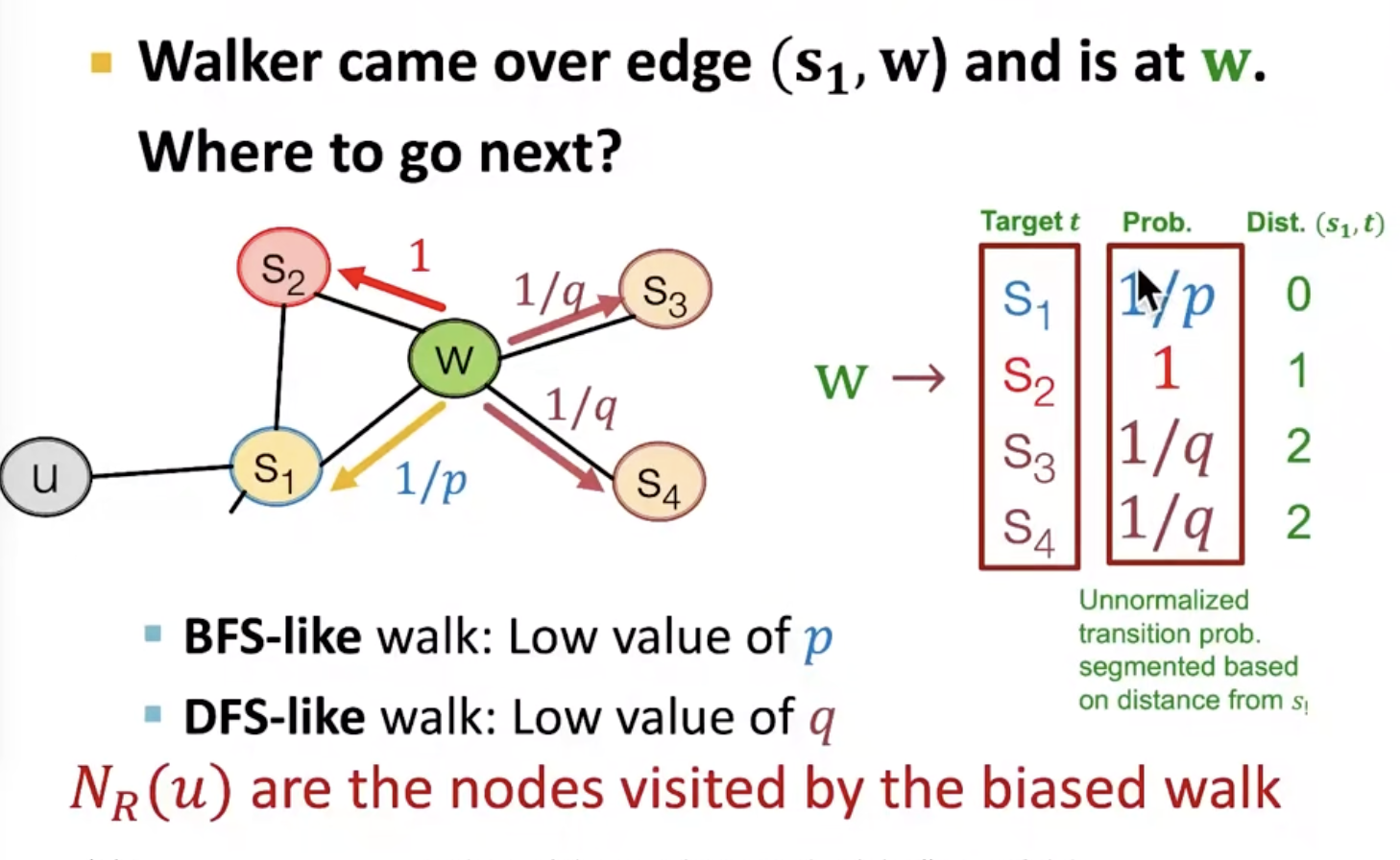
Embedding entire graphs
Approach 1:
Sum (or average) the node embeddings in the (sub)graph G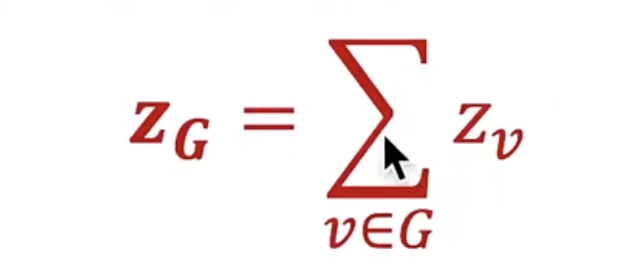
Approach 2:
Introduce a “virtual node” to represent the (sub)graph and run a standard
graph embedding technique.
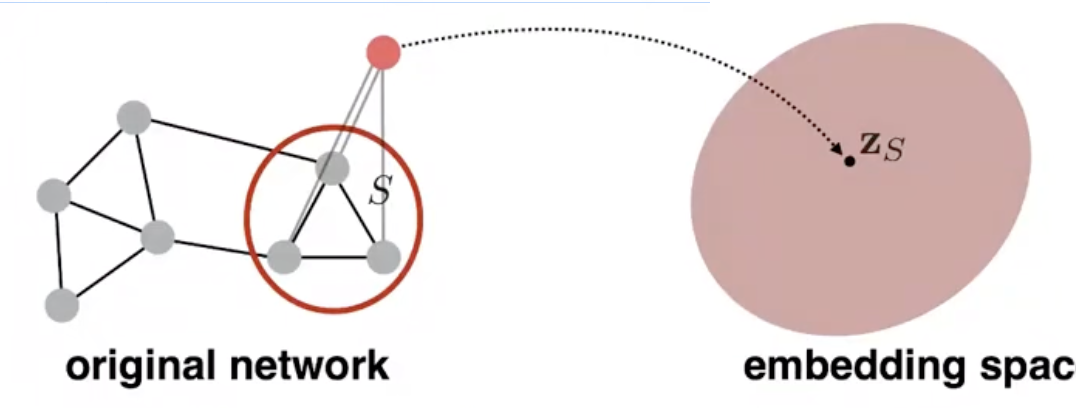
Approach 3:
Anonymous Random Walk:
States in anonymous walks correspond to the index of the first time we visited the node in a random walk.
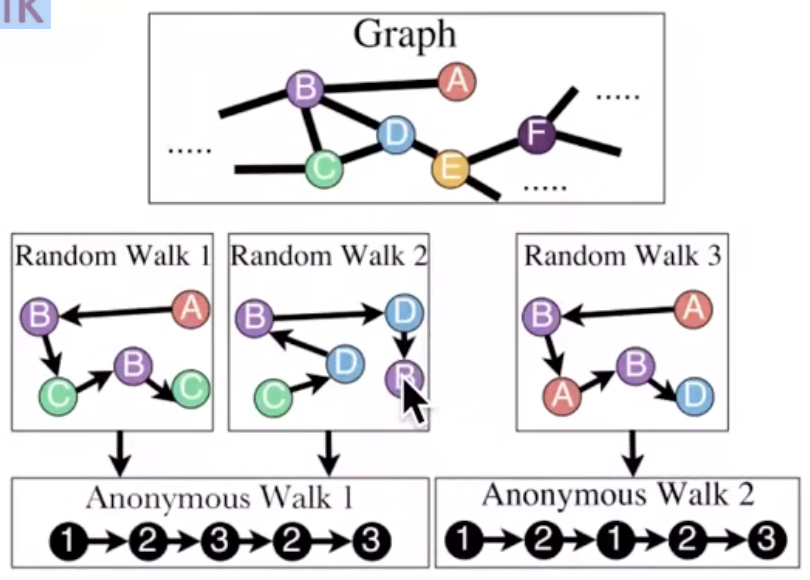
How many random walks m do we need?

Summary: