Logistic Regression_1
Question
Suppose that you are the administrator of a university department and you want to determine each applicant’s chance of admission based on their results on two exams.
理论基础
最基本的逻辑回归底层依然是线性函数,同线性回归,有:
$$
f(x_{1},x_{2},x_{3},…,x_{n})=\theta_{0}+\theta_{1}x_{1}+…+\theta_{n}x_{n}
$$
$$
\begin{array}{}\Theta =\begin{bmatrix}
\theta_{0}\\
…\\
\theta_{n}
\end{bmatrix}\quad
X=\begin{bmatrix}1\\
x_{1}\\
…\\
x_{n}
\end{bmatrix}
\end{array}
$$
$$
f(x_{1},x_{2},x_{3},…,x_{n})=X^{T}\Theta
$$
逻辑回归作用是对数据进行分类,可以通过sigmoid函数将f(x)映射到0-1之间形成一个概率值,并与分界线0.5比较进行预测
$$
p(X)=\frac{1}{1+e^{-f(X)}}
$$
costfunction的构建:
该函数(交叉熵)鼓励将p(x)趋近于1的f(x)往正无穷进行训练,将p(x)趋近于0的f(x)往负无穷进行训练
$$
J(\Theta)= - \frac{1}{m} \sum_{i}^{m} (y_{i} ln{}^{p(X)} + (1 - y_{i}) ln{}^{(1-p(X))})
$$
梯度下降类似线性回归进行偏微分,结果为:
j=0时,x_j=1
$$
\theta_{j}=\theta_{j}-\frac{\alpha }{m}\sum_{i=1}^{m}(p(x^{i})-y^{i})x_{j}^{i}
$$
设定迭代次数进行循环,接收最终的theta,可得:
$$
p(X)=\frac{1}{1+e^{-(X^T\Theta)}}
$$
$$
\hat{y}=1 \quad if \quad p(X)>0.5 \quad else \quad \hat{y}=0
$$
数据读取处理
1 | import numpy as np |
| Exam1 | Exam2 | Accepted | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 34.623660 | 78.024693 | 0 |
| 1 | 30.286711 | 43.894998 | 0 |
| 2 | 35.847409 | 72.902198 | 0 |
| 3 | 60.182599 | 86.308552 | 1 |
| 4 | 79.032736 | 75.344376 | 1 |
1 | fig,ax=plt.subplots() |
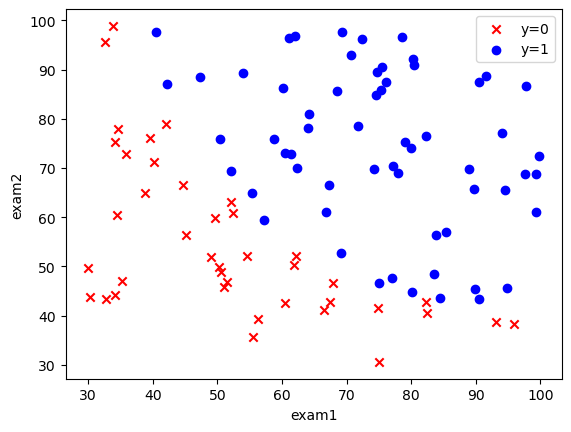
1 | def get_Xy(data): |
构造损失函数
1 | def sigmoid(z): |
1 | def costFunction(X,y,theta): |
1 | theta=np.zeros((3,1)) |
构造梯度下降
1 | def gradientDescent(X,y,theta,alpha,iters): |
迭代得到结果
1 | alpha=0.004 |
1 | theta_final |
1 | def predict(X,theta): |
准确率预估
1 | y_=np.array(predict(X,theta_final)) |
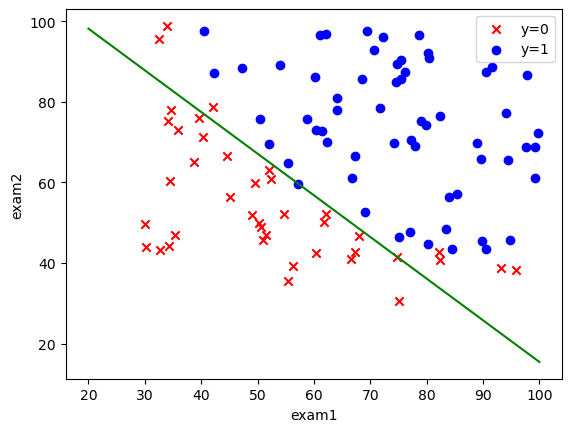
画图
1 | coef1=-theta_final[0,0]/theta_final[2,0] |
Site
代码(Jupyter)和所用数据:https://github.com/codeYu233/Study/tree/main/Logistic%20Regression_1
Note
该题与数据集均来源于Coursera上斯坦福大学的吴恩达老师机器学习的习题作业,学习交流用,如有不妥,立马删除

